
Radon: Understanding the risks and protective measures that should be taken
What is Radon?
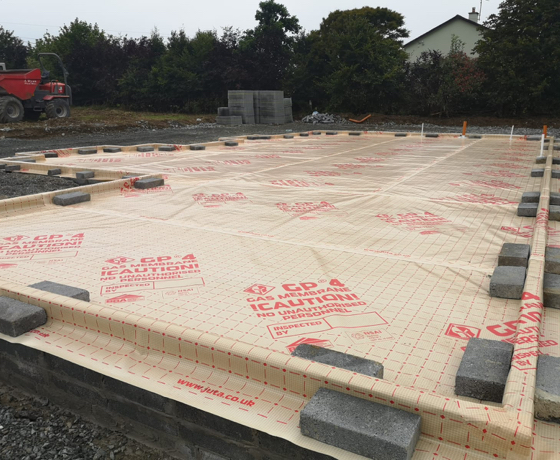
Radon (Rn) is a natural, odourless and colourless radioactive gas formed by small amounts of uranium that occur naturally in rocks and soils. It moves through cracks in the earth and finds its way into the atmosphere which is harmless to the population. However, where radon concentrates build up inside a building, it can cause lung cancer and currently attributes to over 1100 deaths per year in the UK.
Radon is measured in becquerels per cubic metre of air (Bq/m-3) and the average home measures around 20 Bq/m-3. The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) recommends that radon levels should be reduced in homes where the average is more than 200 Bq/m3, known as the action level. New homes should be designed to ensure radon concentrations are less than 100 Bq/m-3, known as the target level.
UK Maps of Radon
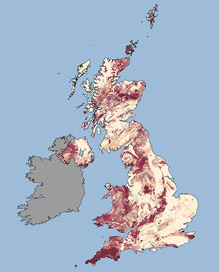
The radon maps with the latest update in December 2022 released by the UKSHA, for the first time in 10 years, provides a postcode search with 1 km keys and indicates the percentage risk for the area - the darker the shading, the higher the risk of radon the area. A link to the interactive UK maps of radon can be found in the appendix. [1]
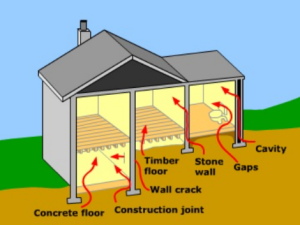
Radon Protection Requirements as per BR 211: 2023
There are two protection levels dependent on the risk laid out in the UK radon maps with protection measures required:
The radon basic protection comprises of a well installed radon barrier linked to a radon resistant damp proof course which will act as a dual-purpose barrier for both damp and radon resistance.
The radon full protection comprises of a well installed radon barrier linked to a radon resistant damp proof course, as per the basic protection, together with the provision of a ventilated subfloor void or radon sumps, which can be activated by fan(s) as per the project designer’s requirements.
Radon Membranes
BR 211:2023 guidance advises the use of 400 microns or above (0.4mm) according to construction conditions identified in the design. British Standard 8485: 2015 + A1: 2019 states that a polyethylene membrane material less than 400 microns is unlikely to withstand construction damage post installation.

The BBA also made the following statement in September 2020: “the BBA we have now reviewed our position on gas membranes and have decided to formally adopt the above thickness recommendation by the BS 8485 drafting panel as a minimum requirement for BBA certification of polyolefin membranes for use in gas control applications, including those certified for the control of radon gas”.[2]
It is also important to note that some of the radon barriers available on the market are recycled and it is recommended to check the manufacturers technical data, including BBA Certification, to confirm the membrane is manufactured from virgin polymer and ensure continuity of raw materials in the manufacturing of the membranes, to provide adequate product warranty for the lifetime of the building.
Membrane Protection
It should also be noted that the radon membrane should be protected from follow-on trades either by insulation being installed over the membrane or a 300g non-woven geotextile. Consideration should be made to protect below the membrane dependent on the condition of the prepared subgrade.
Verification
Another notable change in BR211: 2023 advises that the radon protection measures should now have the installation of the radon protection third party verified, prior to placement of cover.
Information to be provided to the homeowner
The BRE (Building Research Establishment) recommends that the purchaser of a building is informed of the following:
Warranty Providers
New dwellings covered by a NHBC warranty are required to have radon protection measures in accordance with the updated mapping in line with Building Regulations.
Whilst Premier Guarantee Technical Manual Section 1 – Ground conditions currently advises that adequate steps have been taken to identify radon and protective measures have been put in place either:
Protection Provisions for Extensions and Basements
Radon gas is heavier than air and hydrogen and therefore creates a higher risk of elevated radon levels irrespective of the geographical location within the basement. This is due to being in contact with the ground, together with limited ventilation. Therefore, there is a requirement for basements to be designed to protect the occupants from radon ingress as well as waterproofing the structure to create a dry useable space as per BS 8102: 2022 guidelines.
There is also a need to provide radon protective measures in extensions and conservatories that fall into high levels of radon. If the existing house being extended already has radon protection, a similar level of protection should be provided to the extension.
How Galaxy Insulation can assist with radon
At Galaxy Technical Services we provide the complete construction solution and give customers’ confidence through compliance by delivering market leading technical services.
Galaxy Technical Services offers free ground floor U-value calculations - setting out the full build-up specification including radon protection, where required, to achieve compliance. We can also provide gas membrane proposal project packs to meet BS 8485: 2015 + A1: 2019 standards.
We provide an impartial view on regulatory compliance considering the below key areas:
Get in touch and speak to our knowledgeable technical and sales team by emailing technicalservices@galaxyinsulation.co.uk
More information about Radon can be found at: https://radonassociation.co.uk/
Appendix
[1] https://www.ukradon.org/information/ukmaps
[2] Minimum Thickness of Membranes for use as Radon Barriers - BBA (bbacerts.co.uk)